Tag: blockchain security
-
What Is SHA-256? Explaining the Hash Behind Crypto
SHA-256 turns any data into a fixed 256-bit fingerprint, powering Bitcoin’s immutability, tamper detection and proof-of-work. This piece unpacks how the hash secures crypto networks.
-
What Is a Soft Fork? Exploring Its Impact on Bitcoin
A soft fork is a backward-compatible protocol change that tightens rules without splitting the network. In Bitcoin, it enables upgrades with minimal disruption but depends on miner and node coordination.
-
What Is a Seed Phrase? Essential Crypto Guide
Seed phrases-12 to 24 human-readable words-are the master key to your crypto wallet. This guide explains how they work, why they’re critical, and best practices to store them safely.
-
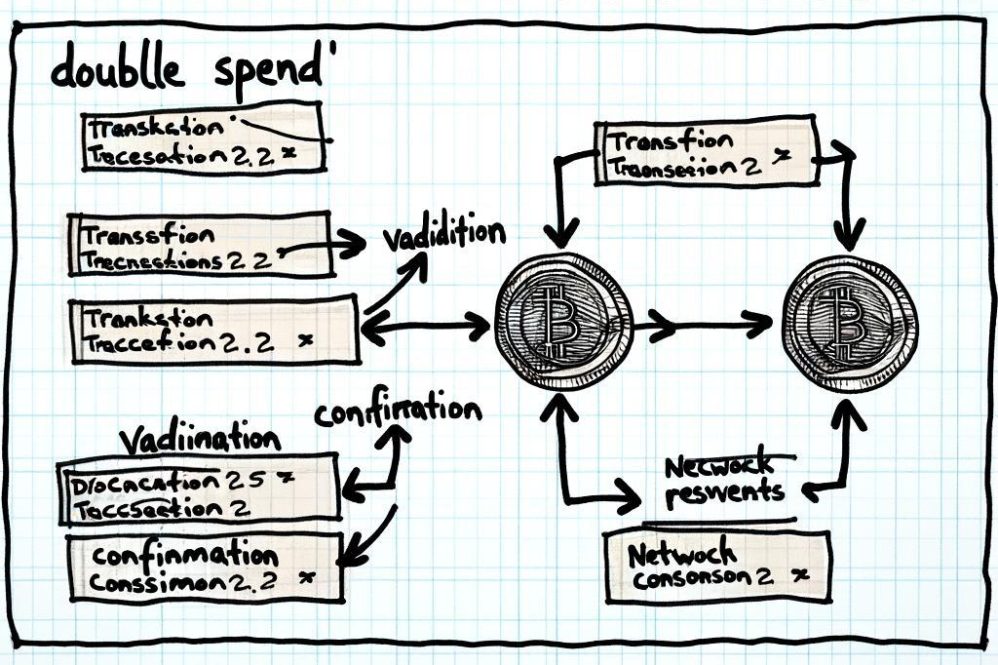
Double Spend Explained: What It Is and How It Works
Double spend is when a digital currency is spent twice. This piece explains how it happens, why blockchain prevents it, common attack methods, and defenses like confirmations and consensus.
-
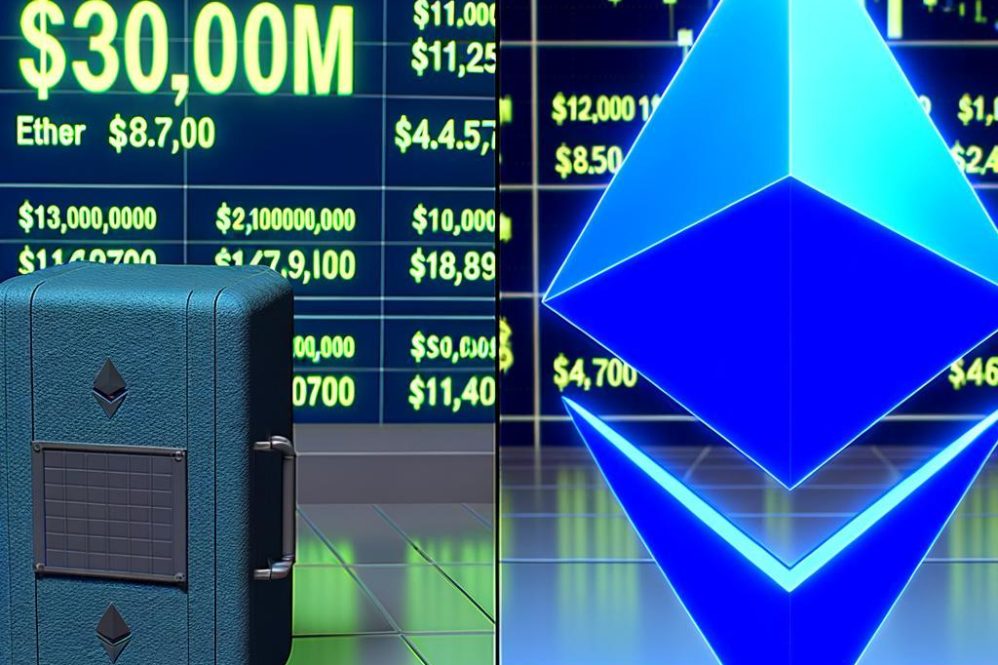
$300M Coinbase hacker buys $18.9M in Ether as ETH breaks above $4,700
Following a $300M Coinbase breach, the hacker moved $18.9M into Ether as ETH surged past $4,700, raising fresh concerns over asset laundering and exchange security among regulators and market participants.
-
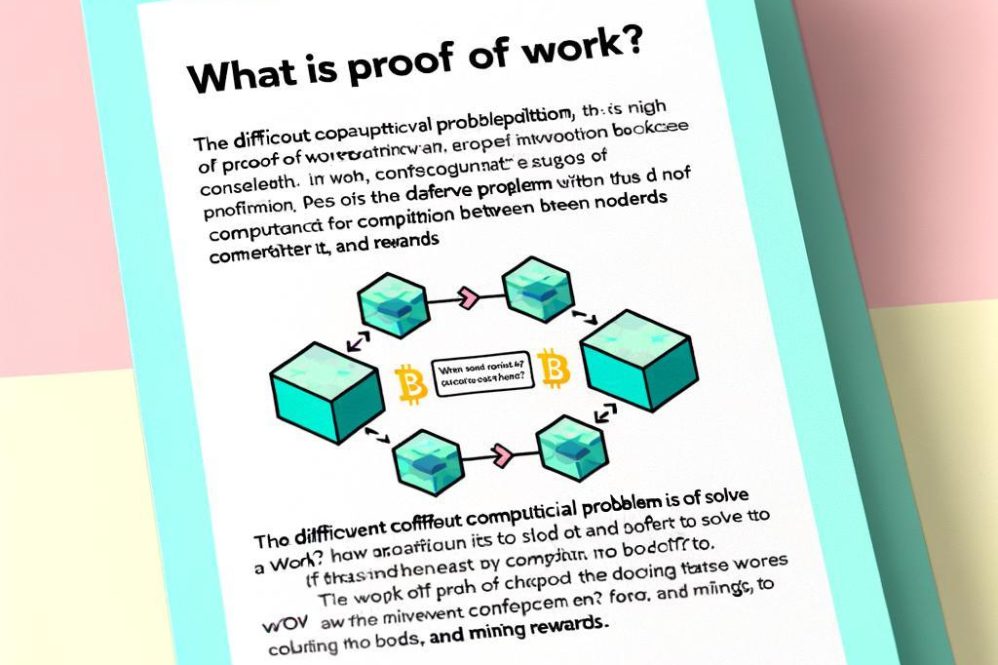
What Is Proof of Work (PoW)? An Educational Guide
Proof of Work (PoW) is a consensus mechanism where miners solve cryptographic puzzles to validate transactions and secure blockchains. This guide explains how PoW works, its energy implications and trade-offs.
-
What Is a Block Reward? Explaining Crypto Incentives
Block rewards are the crypto incentives miners earn for validating transactions and securing networks. They fund operations, shape supply, and influence value as rewards diminish over time.
-
What Is a Hard Fork? Explaining Blockchain Splits
A hard fork is a blockchain split that creates incompatible protocol versions, often spawning a new chain. Stakeholders must choose sides; outcomes reshape governance, security and token value.